Multimodal learning with graphs
In our perspective, we observe that artificial intelligence for graphs (graph AI) has achieved remarkable success in modeling complex systems, ranging from dynamic networks in biology to interacting particle systems in physics. However, the increasingly heterogeneous graph datasets call for multimodal methods that can combine different inductive biases—the set of assumptions that algorithms use to make predictions for inputs they have not encountered during training. Learning on multimodal graph datasets presents fundamental challenges because the inductive biases can vary by data modality and graphs might not be explicitly given in the input.
To address these challenges, multimodal graph AI methods combine different modalities while leveraging cross-modal dependencies. Here, we survey 145 studies in graph AI and realize that diverse datasets are increasingly combined using graphs and fed into sophisticated multimodal methods, specified as image-intensive, knowledge-grounded and language-intensive models. Using this categorization, we introduce a blueprint for multimodal graph AI to study existing methods and guide the design of future methods.
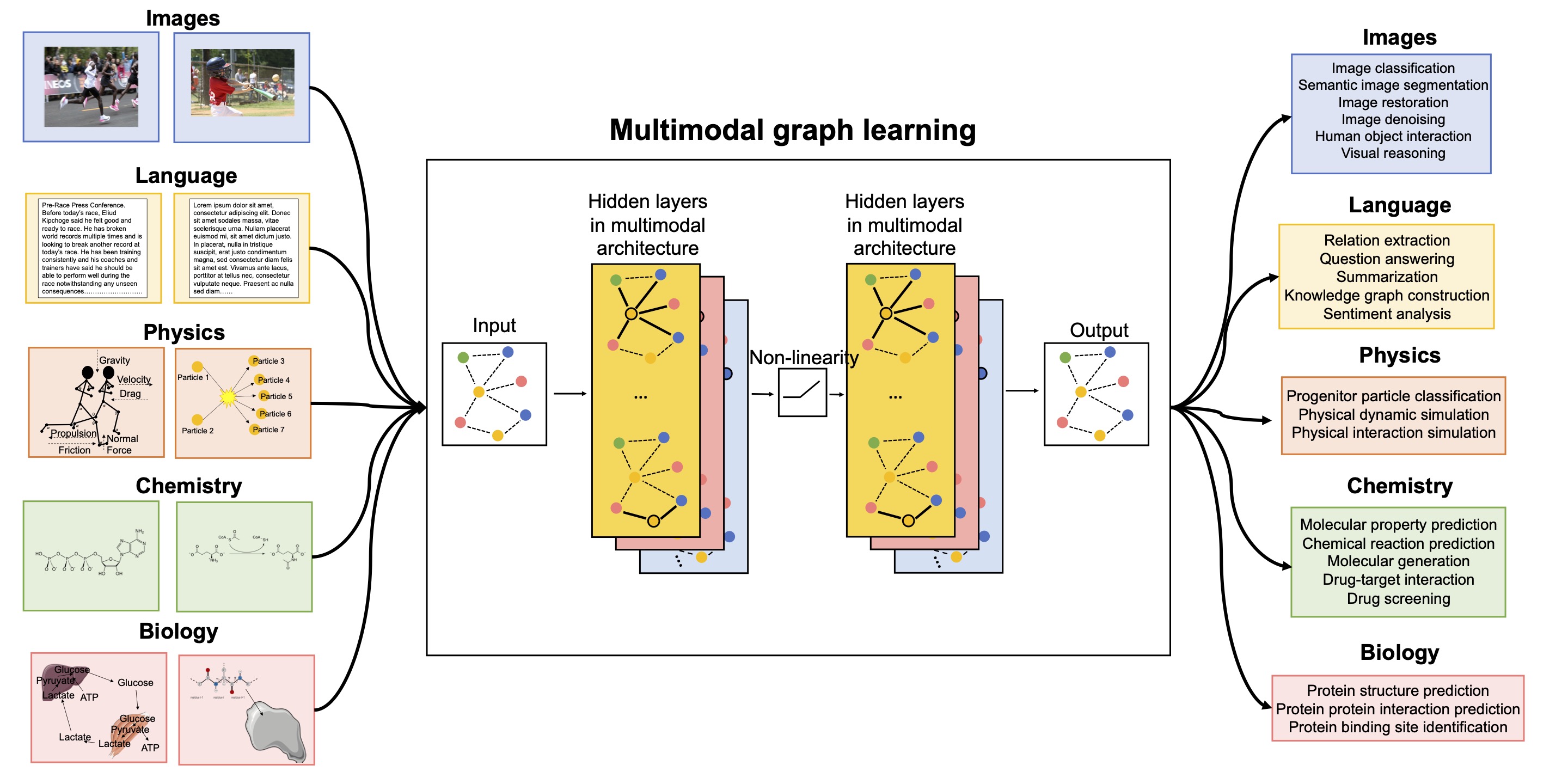 Shown on the left are the different data modalities covered in our multimodal graph learning perspective. Shown on the right are key machine learning tasks for which multimodal graph learning (MGL) has been used successfully.
Shown on the left are the different data modalities covered in our multimodal graph learning perspective. Shown on the right are key machine learning tasks for which multimodal graph learning (MGL) has been used successfully.
Below are studies from our perspective and the community on multimodal graph learning (MGL) and how they fall under the MGL blueprint. This website is meant as (1) a resource to those looking to use MGL for their application but unsure how each component is realized in practice and (2) a map of MGL as an emerging field.
This table is live meaning anyone can submit a study to be considered for this table and we will update the table every week. Entries are grouped by application area.
Use this link to submit a study to be added to this table.
| Method | MGL Component 1: Identifying Entities | MGL Component 2: Uncovering Topology | MGL Component 3: Propagating Information | MGL Component 4: Mixing Representations | Application | Domain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FuNet | Hyperspectral pixels | Radial basis function similarity | miniGCN (GCN mini-batching) | Concatenation/sum/product | Hyperspectral image quad classification | Image |
| GraphFCN | Pixels | Edge weights based on Gaussian kernel matrix | GCN with weighted adjacency matrix | Graph loss added with fully connected network | Image semantic segmentation | Image |
| GSMN | Images/relations/attributes | Visual graph for images combined with textual graph | Node-level and graph-level matching | Similarity function for positive and negative pairs | Image-text matching | Image |
| RAG GAT | Super-pixels | Region adjacency graph | Graph attention network | Sum pooling combined with an MLP | Superpixel image classification | Image |
| TextGCN | Words/documents | Occurrence edges in text and corpus | GCN | No mixing/single-channel model | Text classification | Language |
| CoGAN | Sentences/aspects | Sentences and aspects as nodes | Cooperative graph attention | Softmax decoding block | Aspect sentiment classification | Language |
| MCN | Sentences/mentions/entities | Document-level graph | Relation-aware GCN | Sigmoid function for probability of entity pairs | Document-level relation extraction | Language |
| GPGNN | Word and position encodings | Generated adjacency matrix | Message passing | Pair-wise representation product | Relation extraction | Language |
| QMGNN | Atoms | Chemical bonds | Weisfeiler-Lehman Network and global attention | Concat with quantum mechanical descriptors | Regio-selectivity prediction | Natural science |
| GNS | Particles | Radial particle connectivity | General graph neural network | No mixing/single-channel model | Particle-based simulation | Natural science |
| MaSIF | Discretized protein surface mesh | Overlapping geodesic radial features | System of Gaussian kernels on a local geodesic system | No mixing/single-channel model | Ligand site prediction and classification | Natural science |
| MMGL | Patients | Modality aware latent graph | Adaptive graph learning based on a GCN | Sub-branch prediction neural network | Disease prediction | Natural science |